Health insurance invest in your happiness
How to understand health insurance
When writing about the meaning of seeking health insurance, you're essentially explaining why people purchase health insurance policies. The core idea is that individuals seek health insurance as a financial protection against unexpected medical costs.
"Seeking health insurance is essentially a proactive step to safeguard one's financial well-being in the face of potential medical expenses."
"By obtaining health insurance, individuals are investing in their peace of mind and ensuring access to necessary healthcare services."
"Health insurance serves as a financial safety net, protecting individuals and families from the devastating costs of unforeseen medical emergencies."
Importance of health insurance:

• Financial Protection:
Detail how health insurance acts as a safety net against exorbitant medical bills.
Explain how it prevents bankruptcy and financial ruin.
• Access to Care:
Highlight the link between health insurance and preventative care.
Discuss how insurance enables timely treatment of illnesses and injuries.
• Improved Health Outcomes:
Explain how regular checkups and early treatment lead to better health.
Discuss the correlation between insurance coverage and overall well-being.
• Peace of Mind:
Emphasize the reduction in stress and anxiety associated with having health insurance.
Explain how it allows individuals to focus on their health, not finances.
Personal anecdotes about benefiting from health insurance
Story 1: Accidental Injury
"I never thought I would need health insurance. When I was young, I always felt that I was in good health and that all illnesses would stay away from me. Until one day, I accidentally sprained my ankle and it was swollen like a steamed bun. I went to the hospital for a check-up and found that the ligament was torn and I needed surgery. If I didn't have insurance, the medical expenses would be enough to make me feel distressed for a long time. Fortunately, the insurance company reimbursed most of the expenses for me, so I can recover with peace of mind. "
Story 2: Treatment of chronic diseases
“I suffer from a chronic disease that requires long-term medication and regular checkups. Without insurance, the high medical expenses would be overwhelming. Thanks to insurance, I can afford expensive medications and go to the hospital regularly for checkups and treatment. Insurance allows me to better control my condition and improve my quality of life. ”
Story 3: Serious illness
“When I was diagnosed with cancer, I was devastated. The high cost of treatment made me feel hopeless. But fortunately, my insurance covered cancer treatment. This enabled me to actively cooperate with the treatment and eventually beat the disease. Without insurance, I might not even have the opportunity to try treatment. ”
Story 4: Pregnancy check-up
"During my pregnancy, I went to the hospital regularly for prenatal checkups, and each checkup cost a lot of money. If I didn't have insurance, these expenses would put me under a lot of financial pressure. Insurance not only reimbursed me for the prenatal checkups, but also allowed me to enjoy better pregnancy care, ensuring the health of me and my baby. "
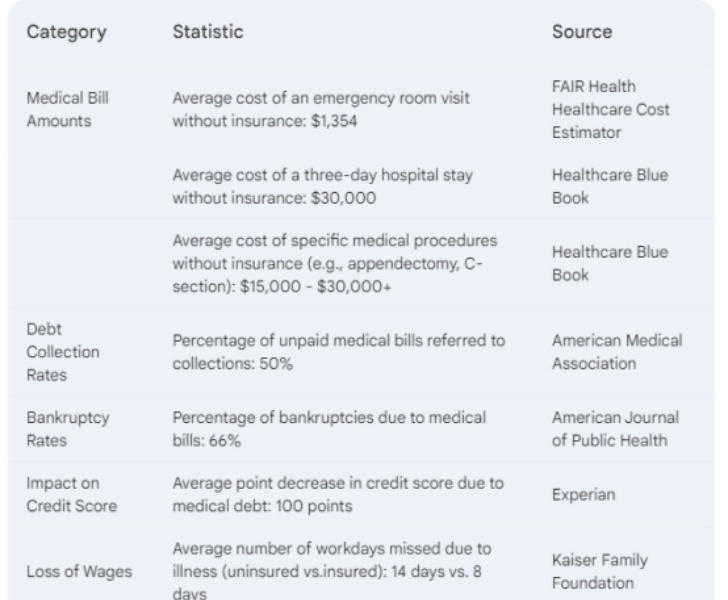
Sure, here are some trial statistics illustrating financial impact of not having health insurance:
Personal views on health insurance
Medical insurance is a financial safety net that protects individuals from the potentially catastrophic costs of illness or injury. It provides access to necessary healthcare services, promotes preventative care, and offers peace of mind.
Essentially, medical insurance provides a sense of security, allowing individuals to focus on their health rather than financial burdens.

Impact of Healthcare on Public Health
Disease Prevention and Contro:
Vaccinations: Prevent outbreaks and reduce disease prevalence.
Screenings: Early detection leads to timely intervention and improved outcomes.
Public Health Campaigns: Educate the public about health risks and promote healthy behaviors.
Treatment and Management of Chronic Diseases:
Access to Care: Ensures individuals with chronic conditions receive necessary treatment.
Disease Management Programs: Help patients manage their conditions effectively.
Research and Development: Drives innovation in treatment and cures.
Emergency Care and Trauma Response:
Immediate Care: Saves lives and prevents disabilities.
Disaster Preparedness: Supports community resilience.
Health Equity:
Access to Care: Reduces disparities in health outcomes. Community Health Centers: Provide care to underserved populations.
Mental Health Integration:
Comprehensive Care: Addresses the whole person, including mental well-being.
Reduced Stigma: Promotes seeking help for mental health conditions.
In conclusion, healthcare is a cornerstone of public health. By focusing on prevention, treatment, and equity, healthcare systems can significantly improve the overall health and well-being of populations.
To mitigate the negative impacts of losing medical insurance, individuals and policymakers can explore options such as:
• COBRA: Provides continued coverage for a limited time after job loss.
• Medicaid: Income-based health coverage for eligible individuals.
• Health insurance marketplaces: Platforms for purchasing individual plans.
• Healthcare reform: Implementing policies to expand coverage and affordability.
Call to Action:
• Inquiries Encouraged: Readers are encouraged to call the hotline, visit the website, or consult a professional for more information.
• Encourage participation: Invite readers to health talks, screening events, or community health projects.
• Encourage sharing: Encourage readers to share information with friends and family.
Encouraging Universal Participation in Medical Insurance
Encouraging universal participation in medical insurance is a complex issue with multifaceted solutions. Here are some key strategies:

Education and Awareness
• Highlight the benefits: Clearly communicate the advantages of health insurance, such as financial protection, access to care, and peace of mind.
• Address misconceptions: Correct misinformation about insurance costs, coverage, and eligibility.
• Promote preventative care: Emphasize how insurance can help individuals maintain good health and avoid costly treatments.
Financial Incentives and Support
• Affordable plans: Offer a variety of plans with different coverage levels and price points to cater to diverse needs.
• Subsidies and tax credits: Provide financial assistance to eligible individuals and families.
• Cost-sharing reductions: Help lower out-of-pocket expenses for individuals with low incomes.
Simplifying Enrollment
• User-friendly platforms: Create easy-to-navigate enrollment processes.
• Open enrollment periods: Ensure sufficient time for individuals to select plans.
• Assistance programs: Offer support for those who need help with enrollment.
Expanding Access
• Community health centers: Increase the availability of affordable care in underserved areas.
• Mobile clinics: Provide healthcare services in remote locations.
• Telehealth: Expand access to care through virtual consultations.
Government Policies
• Mandates: Implement policies that require individuals to have health insurance.
• Employer mandates: Encourage employers to offer health insurance benefits.
• Public health initiatives: Invest in programs that address social determinants of health.
Addressing Underlying Issues
• Poverty and income inequality: Implement policies to reduce poverty and improve economic conditions.
• Health disparities: Target interventions to address health inequities among different populations.
It's important to note that a combination of these strategies is likely to be most effective. Additionally, continuous evaluation and adjustment of policies are essential to ensure optimal outcomes.
